Clean Beauty, Reviva Labs, Skin Care
Does Facial Skin Really Get Thinner as We Age?
If you’ve ever touched your face and wondered whether your skin feels different than it used to – softer, thinner, more fragile – you’re not imagining it. Many people notice these changes as they get older, and there’s real, science-backed biology behind what’s happening. The idea that facial skin becomes thinner with age isn’t just a beauty industry talking point; medical professionals have observed this change for decades. What’s even better? There are meaningful steps you can take to protect and support your skin, help it look healthier, and slow down some of the changes you see.
Your skin is your body’s largest organ, and it’s made up of layers that work together to keep you healthy, strong, and protected from the world around you. As you age, several of these layers – especially the outer surface and the supportive layer beneath – undergo shifts that make them less robust. This doesn’t happen overnight, and it doesn’t look identical on everyone. But a combination of natural aging and environmental exposure do change the way skin looks and feels over time.
Products to Help with Thinning Facial Skin
Why Facial Skin Thins
Your skin has three main layers, and each one plays a role in how your face looks and feels. The top layer, the epidermis, is where dead skin cells shed and new ones take their place. Over time, this layer becomes thinner and the turnover of fresh cells slows down. When this happens, the surface doesn’t bounce back as easily from daily wear and tear.
Below that, the dermis is where collagen and elastin live. These proteins give your skin its strength and elasticity and the ability to spring back when you smile, frown, or laugh. As you age, the production of new collagen slows and existing collagen breaks down faster than it’s rebuilt. The connective tissue becomes more fragile, and the whole dermal layer starts to thin. This doesn’t just change how skin looks; it changes how it feels and responds to bumps, scrapes, and even sunlight.
Another important change happens beneath those layers, in the subcutaneous tissue, essentially a natural fat layer, that gives your face volume and softness. With age, this layer gradually loses fat. That’s why cheeks can look less plump and shadows can appear deeper around the eyes and mouth. While this isn’t the same as thinning skin in the strictest sense (it’s the layer beneath the skin), the visual effect contributes enormously to the perception of thinning.
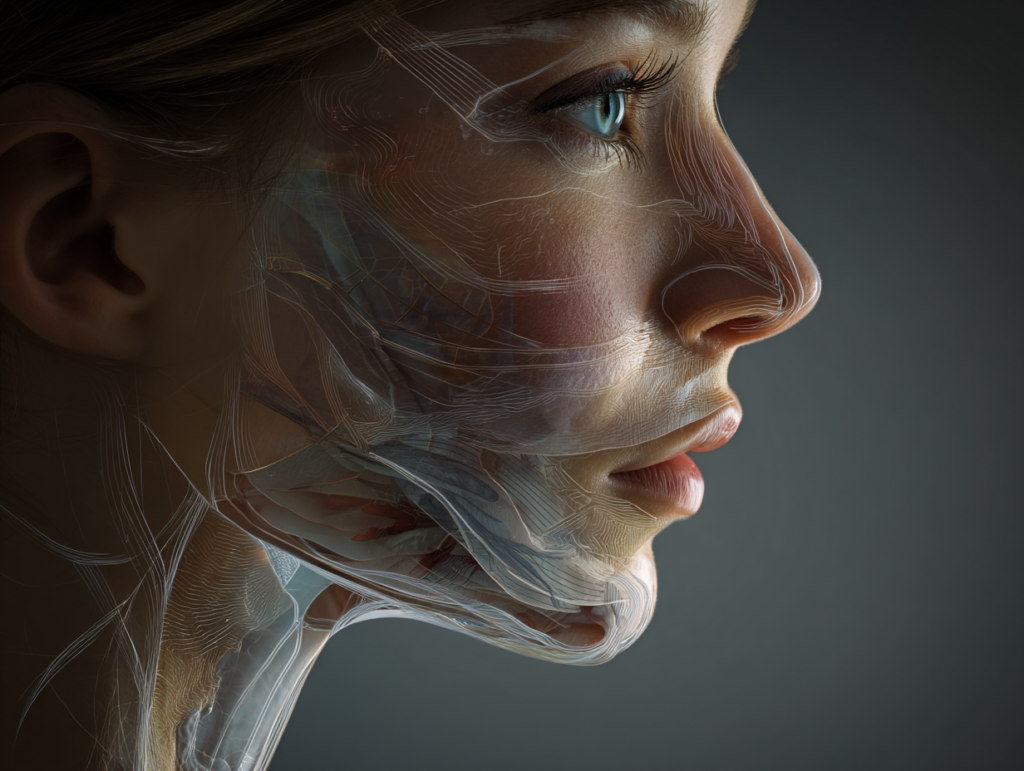

Why These Changes Matter
Thin skin isn’t just a cosmetic concern. As the structure becomes less robust:
- Skin can bruise more easily because the blood vessels underneath are closer to the surface and more delicate.
- Healing from cuts or scrapes can take longer than it used to.
- Dryness, sensitivity, and irritation become more common.
These changes are natural and universal, but that doesn’t mean you’re powerless to make your skin look and feel better. In fact, many steps you can take have strong medical backing.
Sun Protection: The Most Impactful Daily Habit
Of all the external factors that influence skin aging, exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is by far the biggest contributor. UV rays accelerate the breakdown of collagen and damage skin cells long before they’re naturally ready to be replaced. Over years and decades, that cumulative damage accelerates thinning, wrinkles, and fragility.
Daily sun protection is one of the most effective ways to slow visible aging of the skin. Dermatologists recommend using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 every day, even when it’s cloudy or you’re mostly indoors. Wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses also adds layers of defense that sunscreen alone can’t fully provide.
You may think sunscreen is just for preventing sunburn or skin cancer (which it is), but its role in slowing structural damage to collagen and skin cells is enormous. Protecting your skin from the sun is one of the best ways to keep it thicker, stronger, and more resilient as you age.

Hydration and Moisture
As we get older, the skin’s ability to retain moisture also decreases. Oil glands become less active, and your natural barrier that keeps hydration in and irritants out becomes less effective. As a result, skin can feel dry, rough, or tight.
Using a good moisturizer helps reinforce your skin’s barrier. Look for products that contain ingredients like hyaluronic acid, a powerful hydrator that attracts and binds water to the skin, and ceramides, which help seal in hydration. Applying moisturizer after bathing or cleansing, when your skin is slightly damp, gives the best results because it traps moisture before it evaporates.
Drinking enough water and eating foods rich in healthy fats (like fish, nuts, and seeds) also supports skin hydration and overall health. These choices don’t directly make skin thicker, but they make it more comfortable, plump, and less prone to dryness and irritation.
Choose Skincare Ingredients with a Purpose
If you’re building a skincare routine with anti-aging goals, focus on ingredients with real scientific backing:
- Retinoids (like retinol): These vitamin A derivatives encourage cell turnover and can help stimulate collagen production over months of consistent use. Retinoids are among the best-studied ingredients for improving skin texture and resilience.
- Antioxidants (like vitamin C & E): These help protect your skin from environmental stressors and support collagen maintenance.
- Hyaluronic acid: This hydrates the outer layers of the skin and helps it look smoother and fuller.
Use these ingredients consistently and pair them with sunscreen so they can work without increasing sensitivity to the sun.

Lifestyle Habits That Support Healthier Skin
There’s no magic pill to stop skin from aging, but many lifestyle choices make a noticeable difference over time. Smoking, for example, directly contributes to collagen breakdown and weakens circulation, which makes skin look dull and age faster. Quitting smoking and minimizing alcohol intake helps protect your skin’s structure.
Sleep matters more than many people realize. When you sleep, your body goes into repair mode. Hormones that support skin healing and renewal are released, and new skin cells are made. Chronically poor sleep can weaken this repair process.
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and healthy fats supports your body’s natural repair systems. Omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish, flaxseed, and walnuts) help maintain the skin’s barrier and hydration. Vitamin C (from fruits and vegetables) supports collagen production at the biochemical level.
Medical and Cosmetic Options
If you want to go beyond daily care, there are medical and professional options that can create deeper changes in the skin’s appearance. Procedures like microneedling or laser treatments work by stimulating your skin’s repair systems, including collagen production. These options can visibly improve texture and thickness over time when done under the care of a qualified healthcare provider.
Embrace Your Skin at Every Age
Aging skin isn’t a flaw – it’s part of the story you’ve lived. As you age, the changes your skin undergoes are a blend of biology, environment, and lifestyle. While you can’t stop aging altogether, many of the steps above help you protect your skin, support its resilience, and feel confident in your skin’s appearance at every stage of life.

Frequently Asked Questions
Why does facial skin thin with age?
Facial skin thins because the layers that give it structure – especially collagen and elastin – decrease in both amount and strength as you get older, and the outer layer sheds cells more slowly.
Can skincare products actually help skin thickness?
Yes. Ingredients like retinoids and antioxidants support collagen production and protect against environmental damage, which can improve how skin looks over time.
At what age do these changes start?
Skin aging begins as early as your late 20s or 30s, slowly progressing over decades.
Is there any way to reverse thinning skin?
There’s no way to fully reverse thinning skin, but sunscreen, consistent skincare, and professional treatments can slow its progression and improve appearance.
Does diet really impact skin aging?
Yes. A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and healthy fats supports your skin’s repair systems and hydration, which helps skin look healthier.