Sorbitol
Derived from fruit and/or algae to stabilize and give a lubricant feeling to lotions. It is non-toxic.
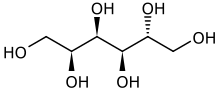
Sorbitol (/ˈsɔː(r)bɪtɒl/), less commonly known as glucitol (/ˈɡluːsɪtɒl/), is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste which the human body metabolizes slowly. It can be obtained by reduction of glucose, which changes the converted aldehyde group (−CHO) to a primary alcohol group (−CH2OH). Most sorbitol is made from potato starch, but it is also found in nature, for example in apples, pears, peaches, and prunes. It is converted to fructose by sorbitol-6-phosphate 2-dehydrogenase. Sorbitol is an isomer of mannitol, another sugar alcohol; the two differ only in the orientation of the hydroxyl group on carbon 2. While similar, the two sugar alcohols have very different sources in nature, melting points, and uses.
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4R,5R)-Hexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol
| |
| Other names
D-glucitol; D-Sorbitol; Sorbogem; Sorbo
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.056 |
| E number | E420 (thickeners, ...) |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Sorbitol |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14O6 | |
| Molar mass | 182.17 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.49 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 94–96 °C (201–205 °F; 367–369 K) |
| 2350 g/L | |
| log P | -4.67 |
| -107.80·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Pharmacology | |
| A06AD18 (WHO) A06AG07 (WHO) B05CX02 (WHO) V04CC01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | > 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) |
| 420 °C (788 °F; 693 K) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
As an over-the-counter drug, sorbitol is used as a laxative to treat constipation.










